The U.S. maternal mortality rate nearly doubled between 2018 and 2021, with COVID-19 as a “contributing factor” in more than 30% of maternal deaths, according to a new report. The report also says medical debt amounts to $88 billion nationwide.
Study
Experts cited several possible reasons for the increases, including higher rates of depression, limited availability of mental health services and the number of guns in U.S. homes.
By 2019, the life expectancy gap between the U.S. and the highest-performing nation had grown to more than six years. The COVID-19 pandemic widened that gap even more, as the U.S. had more deaths from the virus than any other country and has been slower to recover.
Millions worldwide have had long COVID, with dozens of widely varying symptoms including fatigue and brain fog. Scientists still don’t know what causes it, why it only strikes some people, how to treat it -– or even how to best diagnose it.
An international team of researchers wrote in the study that clinical trials may be warranted to investigate whether screening guidelines should recommend Black women start screening at younger ages, around 42 instead of 50.
A nearly decade-long study from the National Bureau of Economic Research looked at births in California. The study found that babies born to the richest Black women were still more likely to die than babies born to the poorest White women.
When you don’t get enough good sleep, the short-term consequences are noticeable — maybe you’re distracted at work or snappy with loved ones. But in the background, irregular and poor-quality sleeping patterns could increase your risk for developing cardiovascular disease, according to a new study.
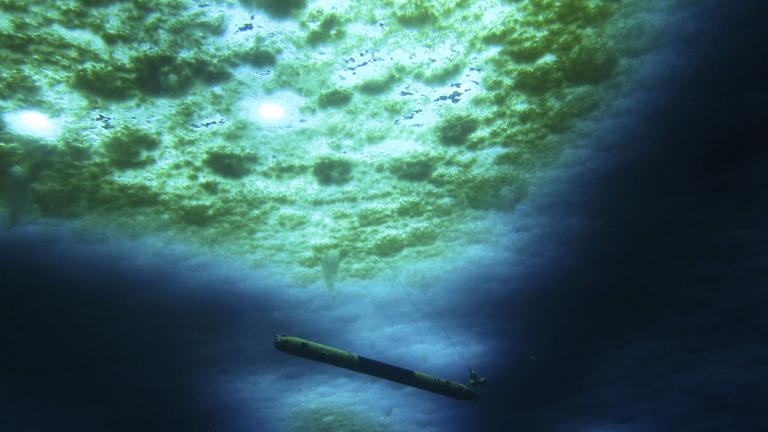
Using a 13-foot pencil-shaped robot that swam under the grounding line where ice first juts over the sea, scientists saw a shimmery critical point in Thwaites’ chaotic breakup, “where it’s melting so quickly there, there’s just material streaming out of the glacier.”
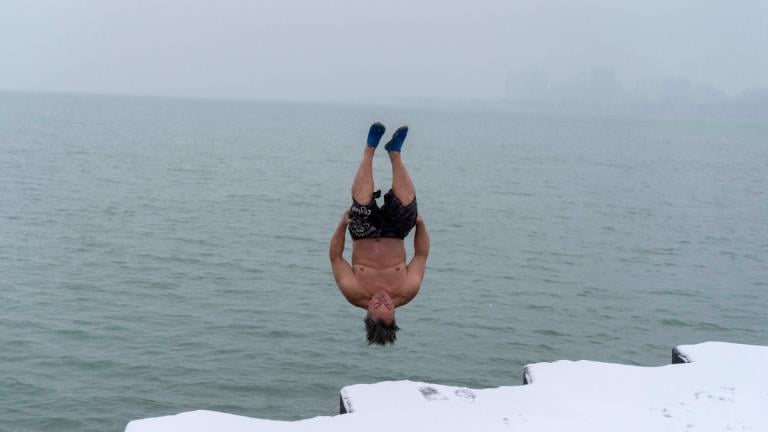
You might call Dan O’Conor an amateur authority on cold water immersion. Since June 2020, the 55-year-old Chicago man has plunged into Lake Michigan almost daily, including on frigid winter mornings when he has to shovel through the ice.
Researchers examined information on the eating habits of people who were part of the UK Biobank, a large biomedical database. Eating patterns were then compared with medical records that listed both diagnoses and deaths from cancer.
With animal fossils hard to come by, the researchers extracted environmental DNA, also known as eDNA, from soil samples. This is the genetic material that organisms shed into their surroundings — for example, through hair, waste, spit or decomposing carcasses.
Japanese drugmaker Eisai and its U.S. partner Biogen had announced earlier this fall that the drug lecanemab appeared to work, a badly needed bright spot after repeated disappointments in the quest for better treatments of the incurable disease.
A recent study from BMJ Global Health says as many as 1.35 billion young people ages 12-34 across the globe are engaging in listening practices that could make them susceptible to hearing loss.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, an independent panel of health care experts, is recommending that adults under 65 get screened for anxiety.
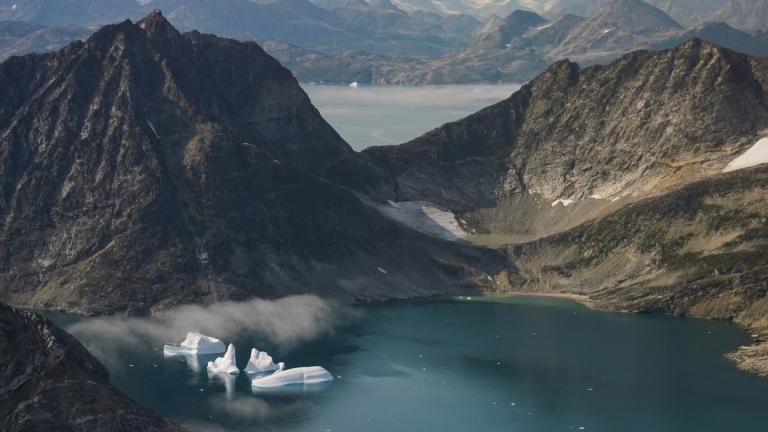
Zombie or doomed ice is ice that is still attached to thicker areas of ice, but is no longer getting fed by those larger glaciers. Meanwhile the doomed ice is melting from climate change, said study co-author William Colgan, a glaciologist at the Geological Survey of Denmark and Greenland.
The Alzheimer’s Association reports that among Black Americans age 70 and older, more than 21% are living with that disease. Pharmaceutical company Eli Lilly is launching a clinical trial of a new drug therapy for those at risk, and they’re looking for participants in Chicago.